In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, IT practitioners stand as the first line of defense against an increasingly sophisticated array of threats. Their role in safeguarding critical assets, data, and infrastructure has never been more crucial. But as the complexity and frequency of cyber attacks escalate, these professionals often find themselves overwhelmed by an ever-growing list of responsibilities and tasks.
Mounting pressure on IT teams
A recent survey by Pluralsight (2024) revealed that a staggering 96% of technologists feel their workload has increased significantly due to the skills gap, with security tasks taking up a substantial portion of their time. This surge in workload isn't just a matter of inconvenience; it's a potential security risk.
When IT practitioners are stretched thin, critical security measures can be inadvertently neglected or delayed.
Patch management, device monitoring, and identity and access control – all fundamental to maintaining a robust security posture – often get buried under the weight of daily firefighting and urgent requests.
The consequences of these delays can be severe. A report from the Ponemon Institute (2023) found that 60% of data breaches in the past year could have been prevented by timely patching of known vulnerabilities. Similarly, a study by Verizon's 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report highlighted that 61% of breaches involved credentials, emphasizing the critical nature of robust identity and access management.
Research also shows that breaches involving stolen or compromised credentials are the most damaging of all attack types.
IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach report revealed that these incidents take the longest to detect and contain - an average of 292 days - and result in an average cost of $4.81 million per breach.
The toll on IT practitioners
The pressure to maintain security while juggling numerous other responsibilities takes a toll on IT professionals. A survey by the International Information System Security Certification Consortium (ISC)² in 2023 found that 51% of cybersecurity professionals reported extreme stress or burnout in their roles. This not only affects their well-being but potentially the quality of their work and, by extension, the organization's security posture.
Orchestration and automation: game changers for overstretched IT teams
So how can organizations ensure these crucial security tasks don't fall by the wayside while also supporting their IT teams? One reliable solution is effective orchestration and automation.
By implementing automation tools and processes, IT teams can streamline routine security tasks, reducing the risk of human error and freeing up valuable time for more strategic initiatives.
4 key orchestration and automation use cases for IT
1. Patch management
Automated patch management systems can scan, prioritize, and deploy critical updates across the network, ensuring timely protection against known vulnerabilities. For instance, Microsoft's recent Patch Tuesday in September 2023 addressed 62 vulnerabilities, including two zero-day flaws. An automated system could swiftly identify affected systems and deploy these critical patches, significantly reducing the window of vulnerability.

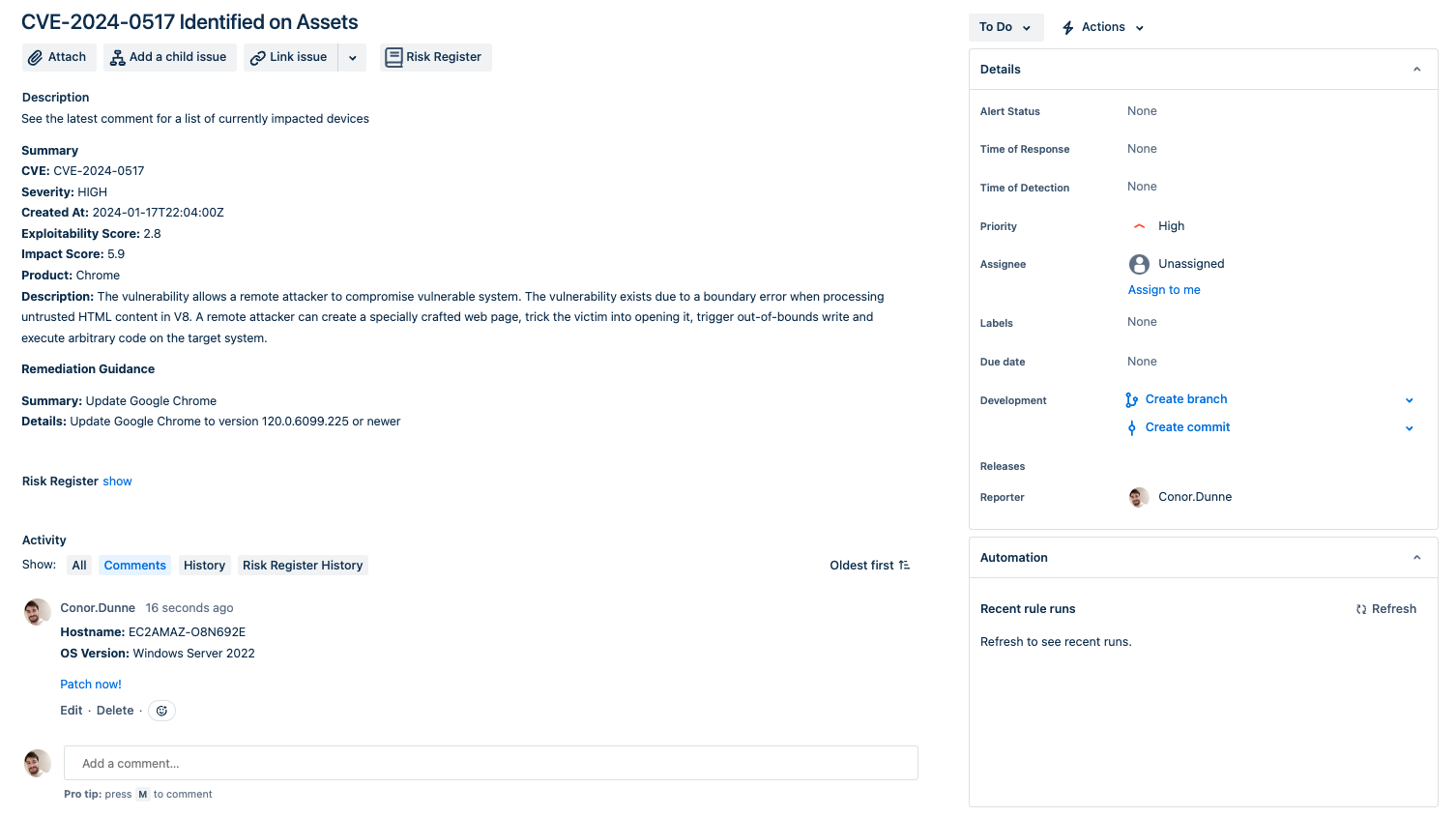
Fetch and record CrowdStrike Spotlight vulnerabilities with Jira
Pull all open CrowdStrike Spotlight vulnerabilities and filter the vulnerabilities by CVE. Then create issues in Jira for CVEs that have not been seen before or reopen closed issues if new machines have been impacted by a CVE. Automox can also be used to initiate patches for identified vulnerabilities.
Tools
2. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
AI-powered IAM solutions can continuously monitor user behavior, flagging anomalies and potential threats in real-time. These systems can automatically enforce multi-factor authentication, manage password policies, and even initiate account lockdowns when suspicious activities are detected. Gartner predicts that by 2025, 70% of new access management deployments will leverage AI-powered analytics and automation capabilities.

Approve user access to Okta or Office 365 using Pages
Set up a self-service portal to enable end users to request user IDs for Office 365 (Microsoft Entra ID) or Okta using Tines pages. Send approval requests to system owners; upon approval, provision the user.
Tools
3. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Automated SIEM tools can collect and analyze log data from various sources across the network, quickly identifying potential security incidents. By automating the initial triage of security alerts, these systems can dramatically reduce the time IT teams spend on false positives, allowing them to focus on genuine threats.
Analyze Elastic alerts, block IPs, and notify in Slack and Tines Cases
Analyze Elastic Security alerts for IP threats using GreyNoise and block malicious IPs with Google Firewall. Communicate the incidents on Slack and log the details in Tines Cases.
Created by
4. Compliance monitoring
Compliance orchestration and automation tools can continuously assess the organization's systems against relevant regulatory requirements, flagging any deviations and even suggesting remediation steps. This is particularly crucial given the constantly evolving regulatory landscape, such as the recent updates to the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) enforcement.


The benefits of orchestration and automation
Implementing these workflow orchestration and automation solutions offers multiple benefits:
Enhanced security
By ensuring critical tasks are performed consistently and promptly, orchestration and automation significantly reduce the risk of oversights that could lead to security breaches.
Improved efficiency
Automation frees up IT practitioners to focus on more complex, strategic tasks that require human insight and creativity.
Reduced burnout
By alleviating the burden of routine tasks, automation can help reduce stress and burnout among IT staff, leading to improved job satisfaction and retention.
Cost-effectiveness
While there's an initial investment in automation tools, the long-term savings in time and potential breach prevention can be substantial. IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023 found that organizations with fully deployed security AI and automation experienced $3.05 million less in breach costs compared to those without.
Case study - how Reddit upleveled their IT automation strategy
The IT team at Reddit serves as a great example of how automation can elevate efficiency and security, offering valuable insights into optimizing device management, patching vulnerabilities, and managing user access at scale.
Watch our webinar with Reddit to learn more about how their IT team is leveraging Tines workflow orchestration and automation platform to reinforce their IT strategy.
What to expect:
Understanding Reddit's approach to automating device management for secure, up-to-date configurations.
How Reddit automates patch management to protect against vulnerabilities with minimal disruptions.
Reddit’s methods for managing user access, ensuring seamless and secure access at scale.
Insights into optimizing IT processes through automation to enhance security and efficiency.
Strengthening security posture with IT orchestration and automation
As we navigate an increasingly complex threat landscape, empowering IT practitioners with the right tools and processes is paramount. By leveraging orchestration and automation, organizations can reinforce their security posture without overburdening their already stretched IT teams. This not only enhances overall security but also creates a more sustainable and efficient work environment for IT professionals.
The future of cybersecurity lies not in working harder, but in working smarter. By embracing orchestration and automation solutions, organizations can ensure that their IT practitioners are equipped to face the challenges of tomorrow's threat landscape, today.
Watch our webinar, How Reddit upleveled their IT automation strategy.