The individual case view contains several key components, organized by purpose:
Core configuration
Case Name: The unique title of the case.
Case ID: The unique identifier of the case.
Assignees: Users designated to manage the case. You can assign or reassign individuals directly within the Case interface.
Status: Indicates the current state of the case, such as "To do," "In progress," or "Done." This helps in tracking the case's lifecycle.
Priority: Reflects the urgency of the case, aiding in prioritization and resource allocation.
Tags: Keywords or labels that categorize the case, facilitating filtering and reporting.
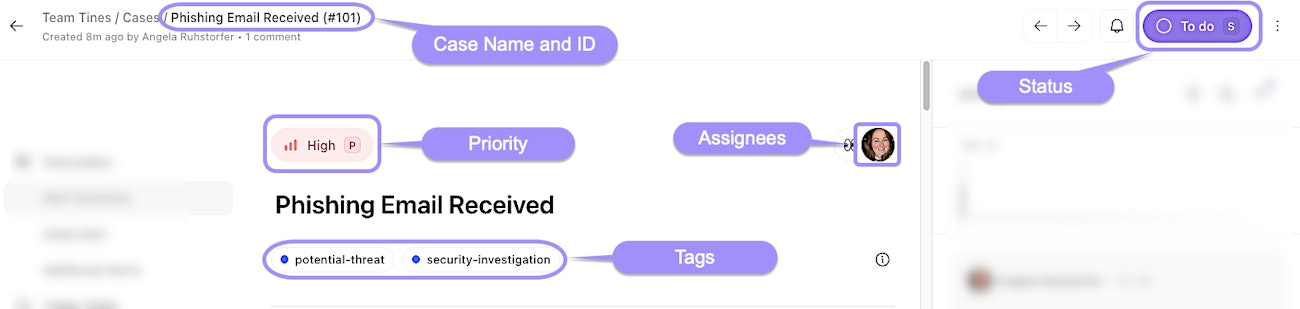
UI locations of core case configuration settings within an individual case.
Details and descriptions
Description: A rich-text field supporting Markdown, allowing detailed documentation of the case's context, history, and actions taken.
Notes: A log of important information or updates related to the case that you want to highlight.
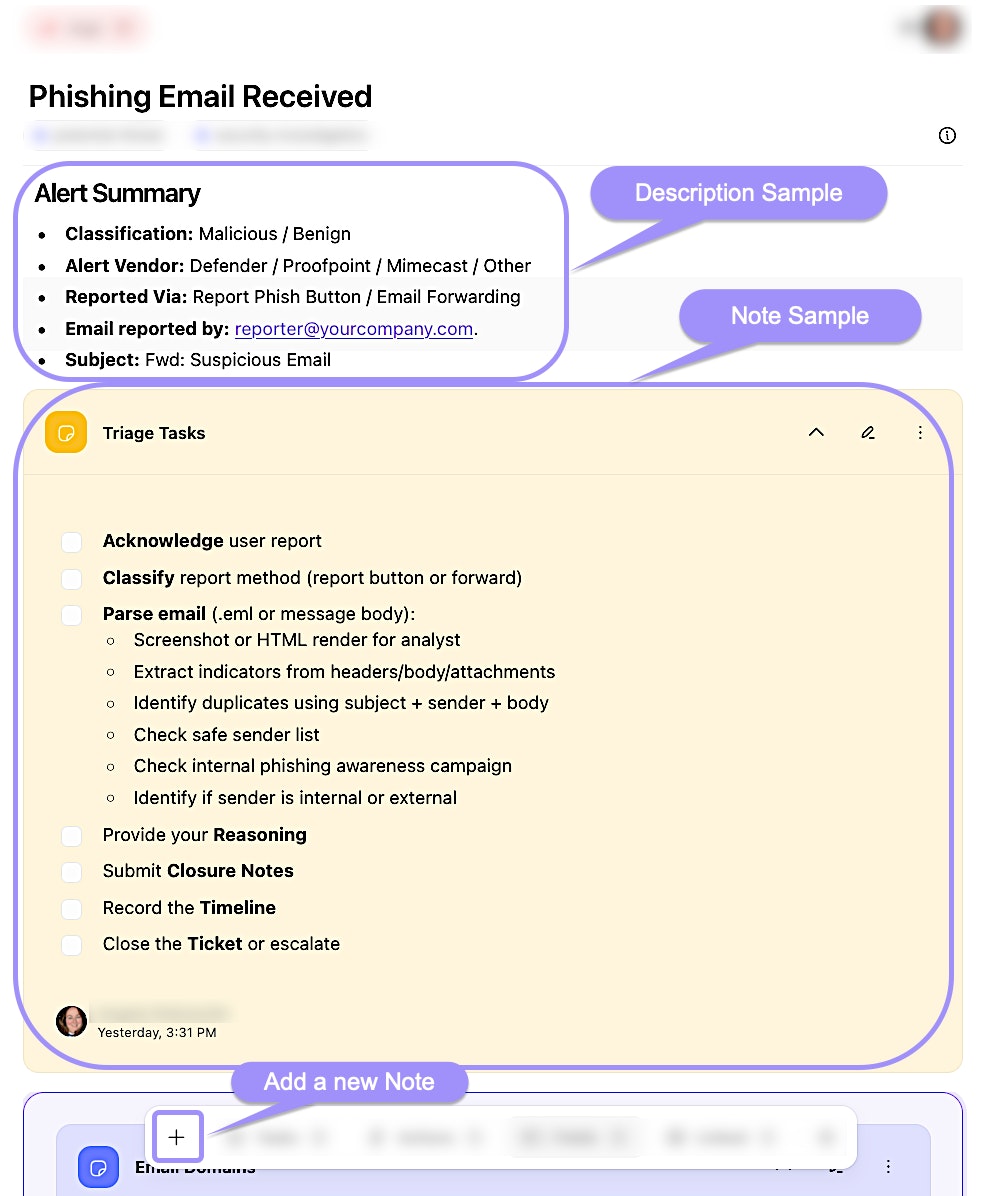
UI locations of the case description and note features within an individual case.
Relationships and dependencies
Linked cases: Associations with other cases, enabling visibility into related incidents or tasks.
Records: Data captured from Tines story runs, attached to the case as artifacts. These records can provide context and evidence for the case.
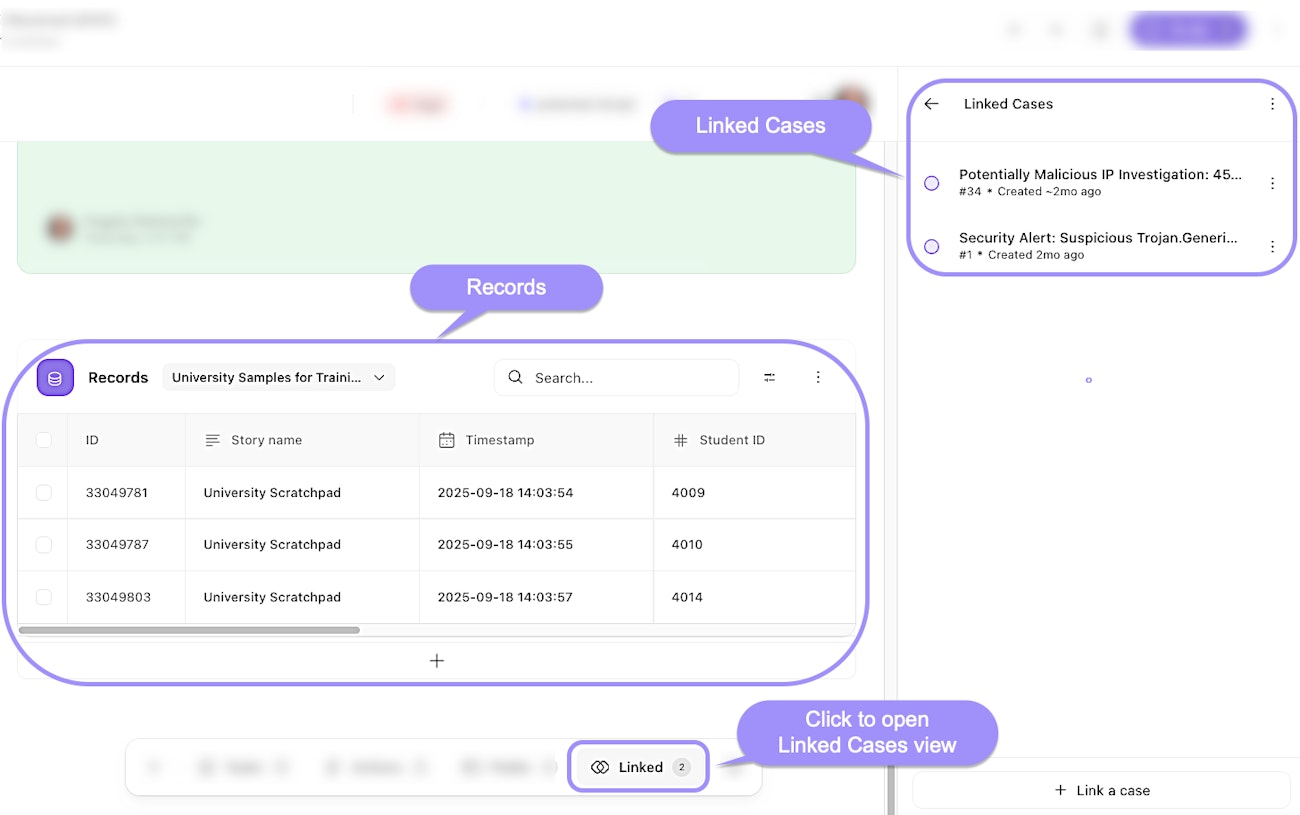
UI locations to records and linked cases features within an individual case.
Custom fields and metadata
Case fields: Custom variables defined at the team level, such as text, number, timestamp, or boolean types. These fields can be referenced within the case description or comments by typing "@" followed by the field name.
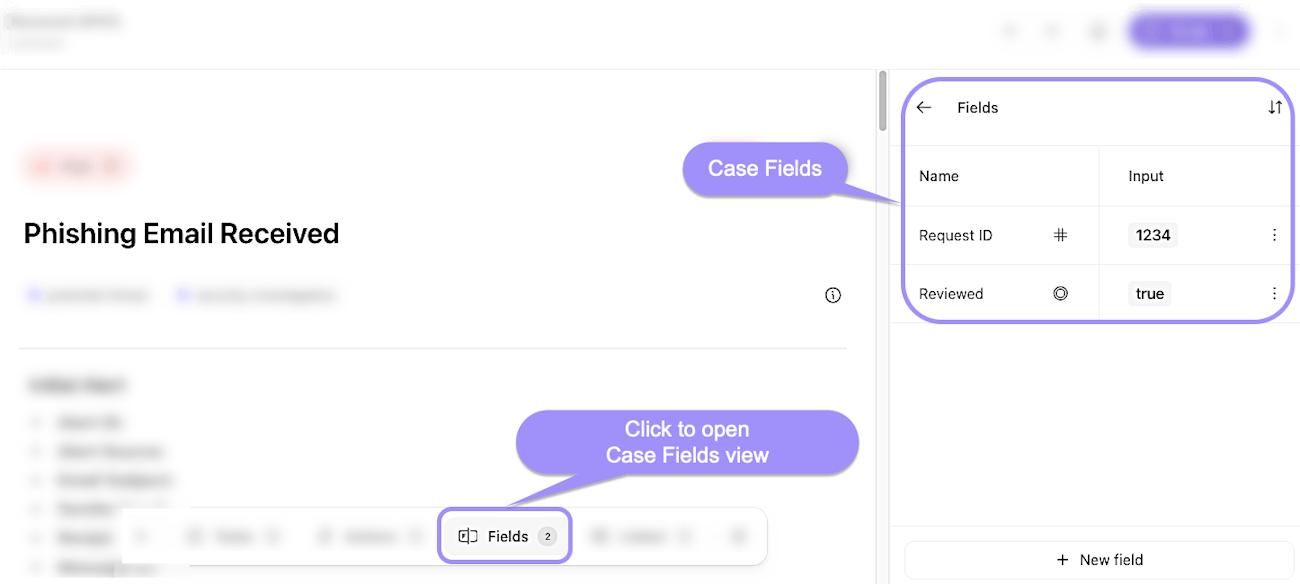
UI locations to the case fields feature within an individual case.
Metadata: Key-value pairs that you can create, providing additional structured information about the case.
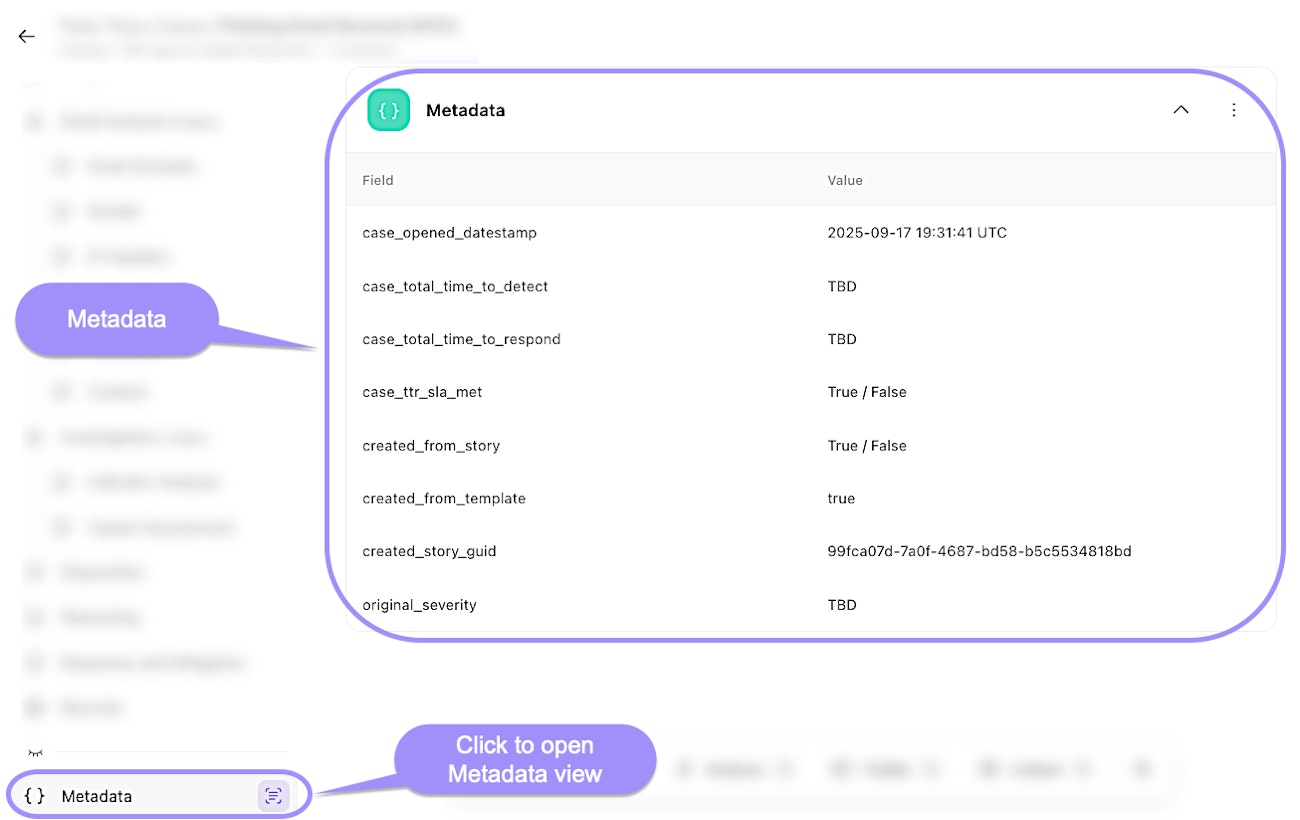
UI locations to the case metadata feature within an individual case.
✋ Try this: Add a case field
Notifications
Subscriptions: Users can subscribe to a case to receive notifications about updates and changes. This ensures relevant stakeholders are kept informed. We’ll look over this more later on in this module.
Automation
Case actions: Defined tasks or operations that can be triggered within a case, such as sending a webhook or opening a page (these elements exist in a story). These case actions facilitate automation and integration with other systems.
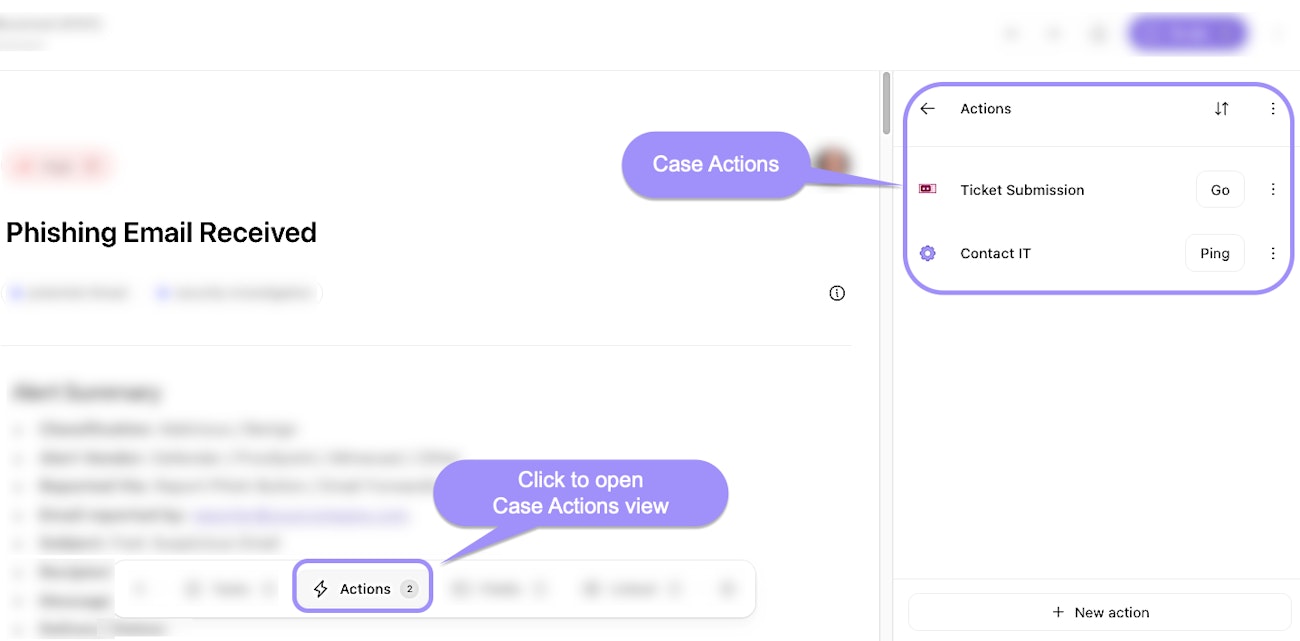
UI locations to the case actions feature within an individual case.
✋ Try this: Add a case action
Closure and compliance
SLA (Service Level Agreement): Defines the expected resolution time for the case based on its priority. Tines tracks SLA compliance and can trigger alerts when SLAs are approaching or have been exceeded. Team-wide SLA configurations can be set up via case settings.
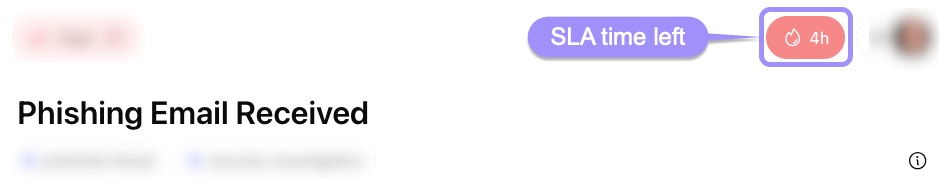
UI locations to the case SLA feature within an individual case.
Closure requirements: Conditions that must be met before a case can be closed, ensuring that all necessary actions and reviews are completed.
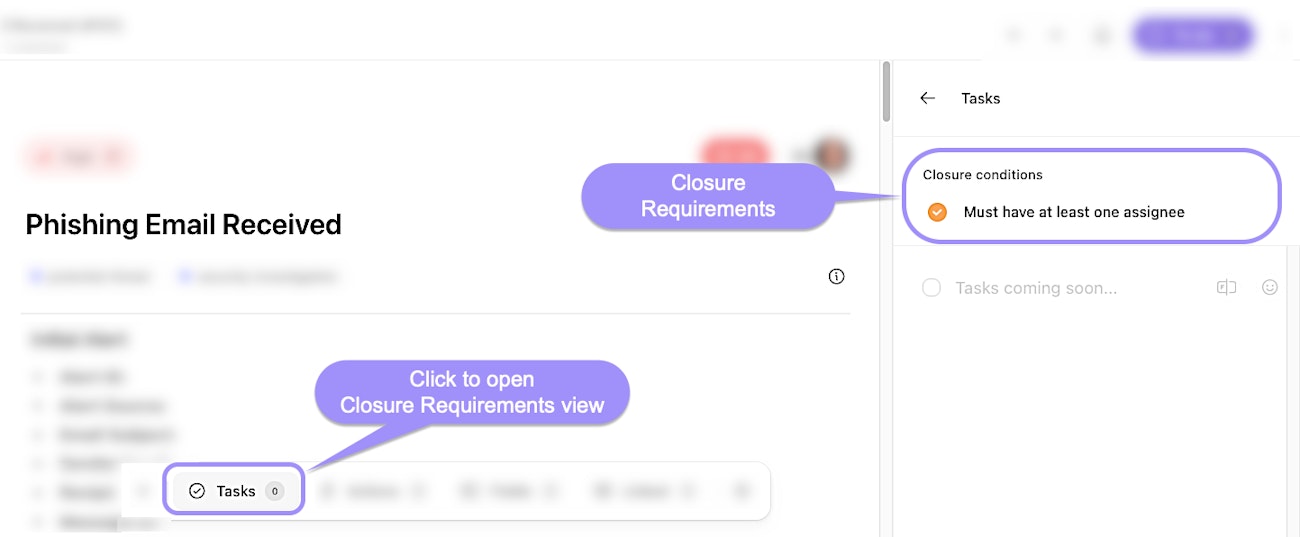
UI locations to the case closure requirements feature within an individual case.
Development and history
Activity: Automatically captures changes like status, priority, tags, assignees, linking/unlinking cases, and record attachments. It provides a filterable timeline so you can see every major update to the case in one place.
Comments: Part of the Activity feed that allows collaborators to add text (with Markdown formatting) and upload files to a case.
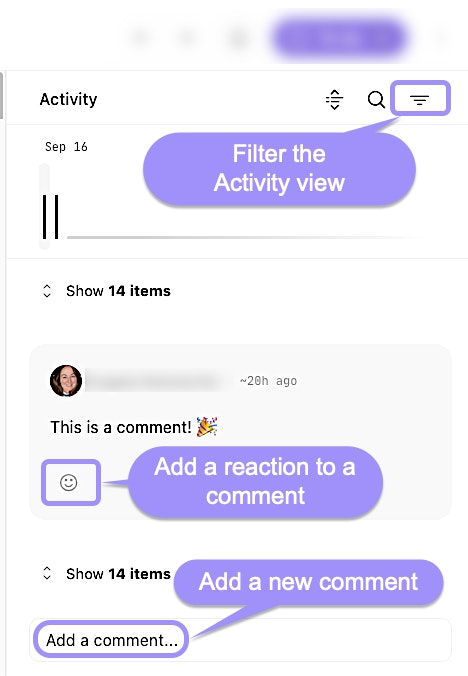
UI locations to the case activity and comments features within an individual case.